- Lesson 5B: Interoperability Standards
- HL7
- HL7 Reference Implementation Model (RIM)
- CCDA
- HL7 Document Standard
- Arden Syntax
- CIMI
- CMS
- FHIR
- Andrei Pop Interview about humanAPI
- Josh Mandel interview (Lead Architect of SMART platform of Harvard Child hospital)
- Recap
Lesson 5B: Interoperability Standards

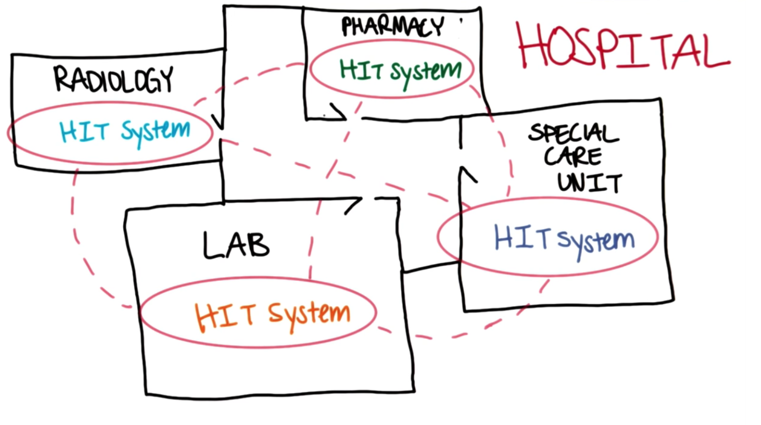
In the last lesson, we learned about data standard and the evolution of standards. In clinical practice, data ( standard and nonstandard) need to be packaged into clinical documents and send via messaging standards. These are the focus of this lesson.
HL7
Health Level-7 or HL7 refers to a set of international standards for transfer of clinical and administrative data between software applications used by various healthcare providers. These standards focus on the application layer, which is “layer 7” in the OSI model. (Health Level 7 - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)



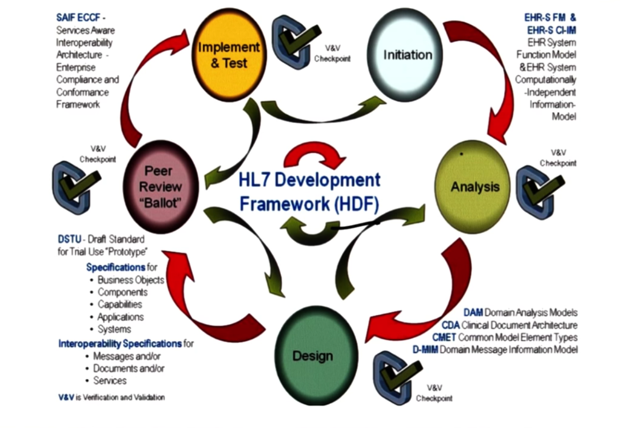
- HDF
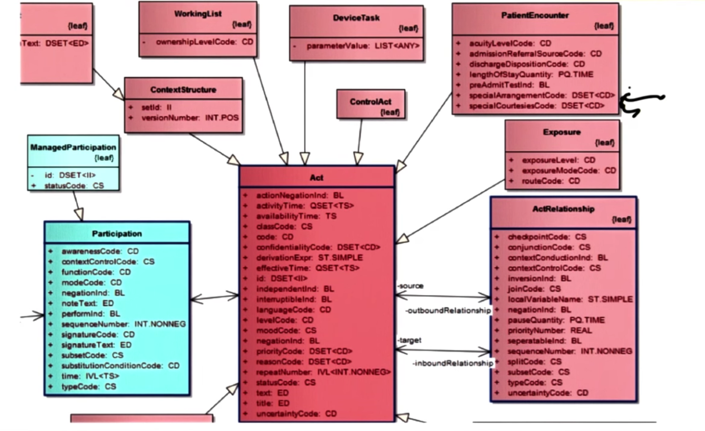
HL7 Reference Implementation Model (RIM)
- RIM can be used to create HL7 ver 3 based XML formatted messages and XML based CCDA documents

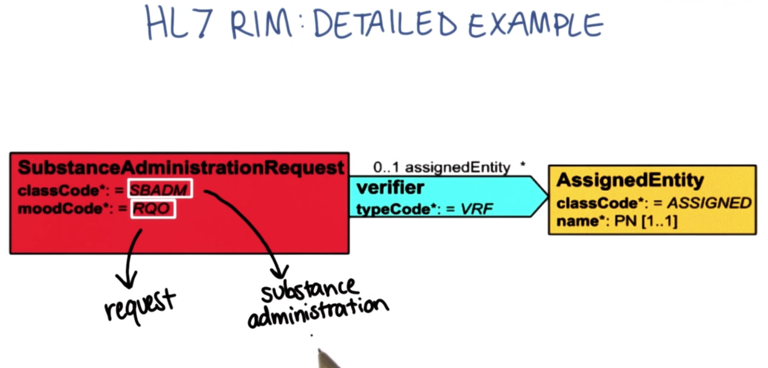
- Here’s the complete RIM example.
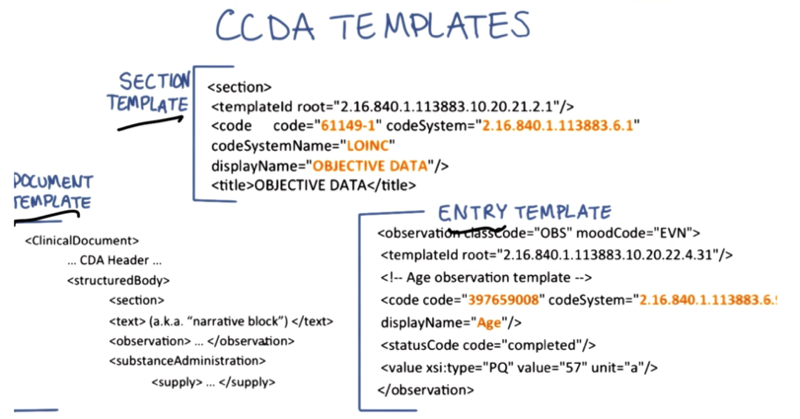
CCDA
- Consolidated Clinical Document Architecture (CCDA)





HL7 Document Standard
- CCDA templates have three subparts: Document template, Section Template and Data Entry Template.
- Templates are reusable XML components

- Hint: the website in the slides does not work, a google search will lead you to the correct answer.




Arden Syntax

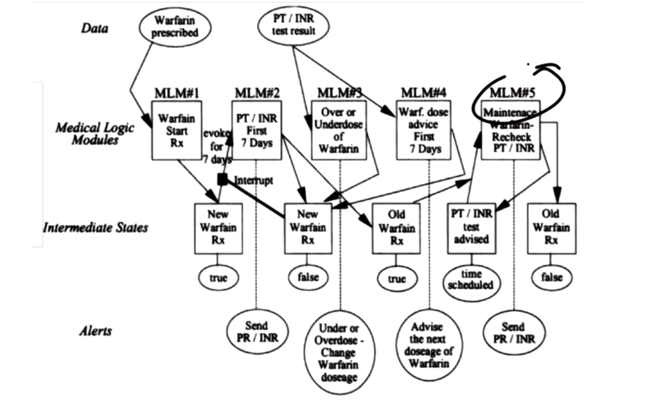
- Each MLM supports one medical decision
- MLM can interact with intermediate States and provide CDS

- Here,
{'dam'="PDQRES2"}must be interpreted by another EMR to get the creatinine level which often could not be performed because of the interoperability issue of EMR softwares.
CIMI

- numerate clinical ideas to achieve consensus among clinicians
- can be used to constructed standard messages and structured documents as components of clinical rules
- automate or facilitate constructing data entry and generating clinical reporting templates
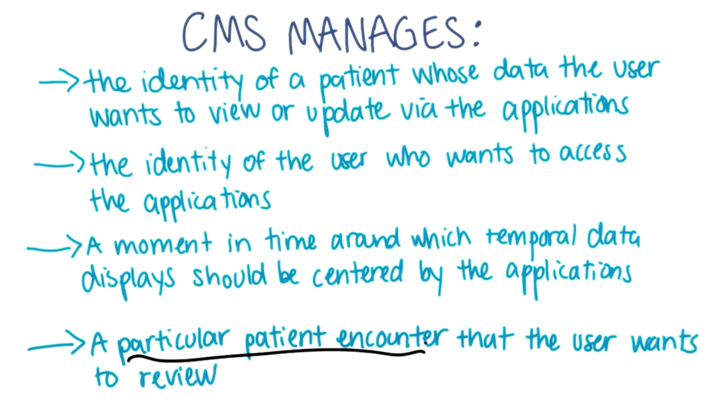
CMS
- CMS wants to integrate applications at the point of use.

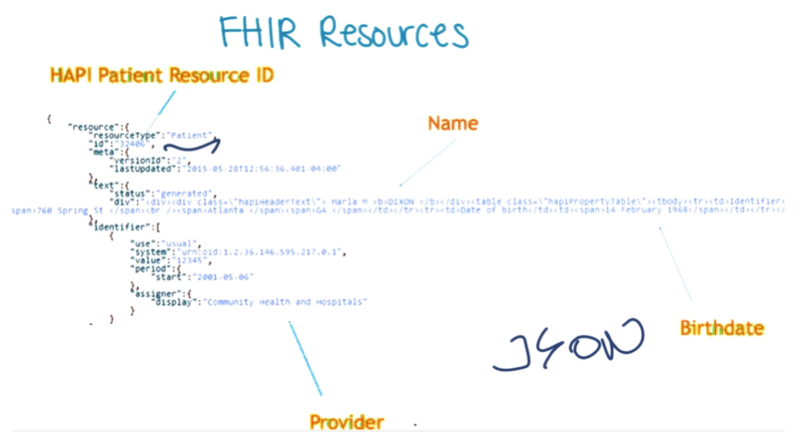

FHIR
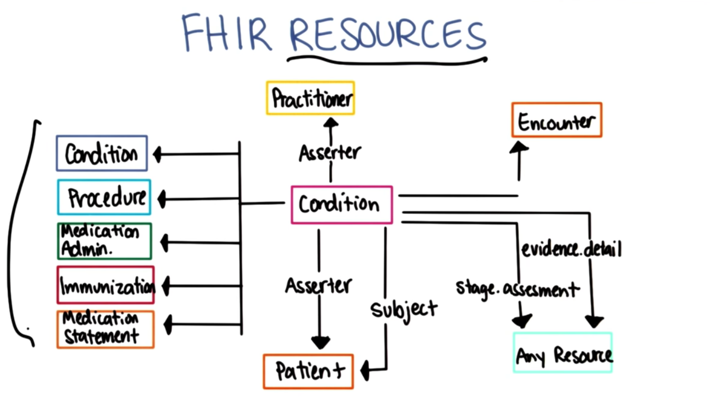
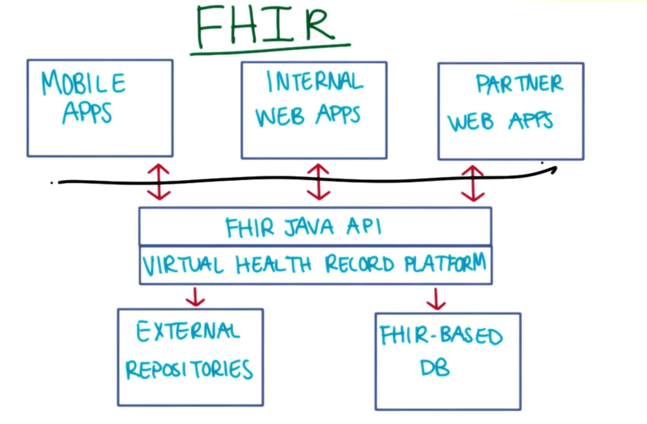
- FHIR is still in development and testing and faces challenges: e.g. trade-off between functionality and complexity;
- FHIR is in its second version and is expected to have 100-150 specifications in the final product.
Andrei Pop Interview about humanAPI
What does HumanAPI do?
It can get health data from multiple sources ( including EHRs, wearable devices), aggregates, normalizes and standardizes them (using HL7) and provided them to EHR, EMRs, etc with users authorization.
The data can be tracked, queried and visualized via API.
It essentially solves the interoperability issue of different vendors of health data generator/provider, etc..
Josh Mandel interview (Lead Architect of SMART platform of Harvard Child hospital)
Q1. Introduction to SMART platform.
A: SMART platform is a project to enable healthcare providers to use the apps they choose to access health data.
Q2. Why is the project important and what approach do you take to solve the problem.
A: Health data of a patient are usually sitting in databases of different health providers, bring the data together and allow apps to be build based on the data. Developers can create tools to better use the data and users can choose the tools they like.
The approach that SMART platform uses is that we build open sets of specifications based on open standards so any developer can use them to build their tools.
Q3. what’s new in the latest version of SMART platform?
A: Many venders, government, independent labs builded apps based on SMART.
Q4: Smart on FHIR.
A: FHIR provides important building block for SMART: 1. FHIR resources(detailed clinical data models); 2. FHIR API base on http and restful.
Demo at
Recap
- Health standards initially were created within the industry and only recently adopted XML and web technology.
- The industry is developing detailed standards and it might making the creation of HIT tools more complex.
2015-09-22 初稿