- preview
- Recording Cases to Case-Based reasoning
- Case Adaptation
- Case evaluation
- Case Storage
- Case Retrieval Revisited
- Advanced Case-Based Reasoning
- Assignment
- Wrap Up
- The Cognitive Connection
preview

Recording Cases to Case-Based reasoning
exercise
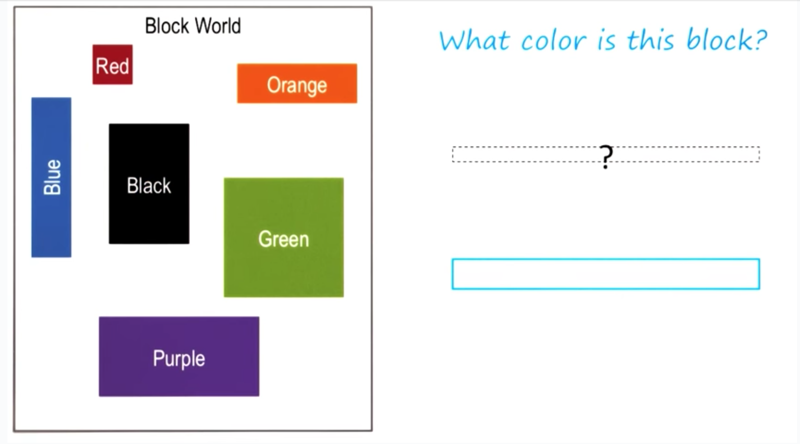
The block is not in the world so “learning by recording cases” does not work. To accomplish the job, one must used to existing cases to learn some rules to reason the solution.
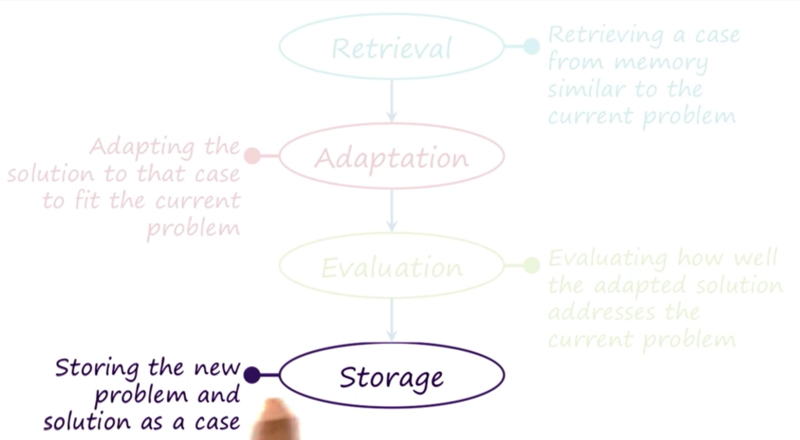
the process of case-based reasoning
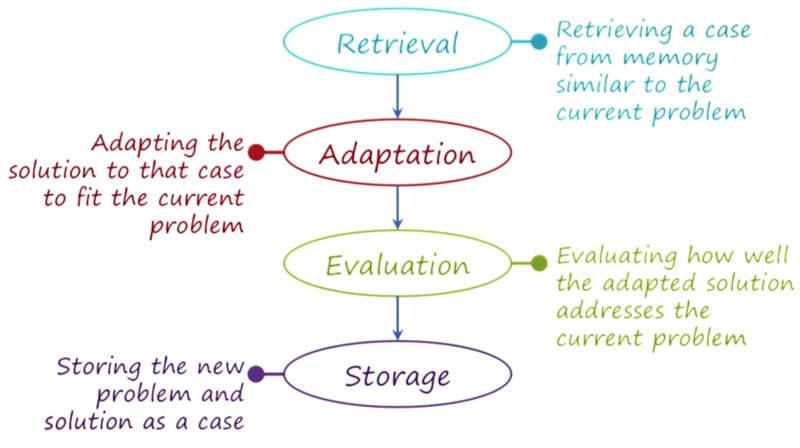
- retrieval: retrieve solutions from memory
- adaption: adapt solution to solve the current problem
- evaluation: evaluate the adapted solution
- storage: save the solution to the case memory for use later
Assumptions of Case-Based Reasoning
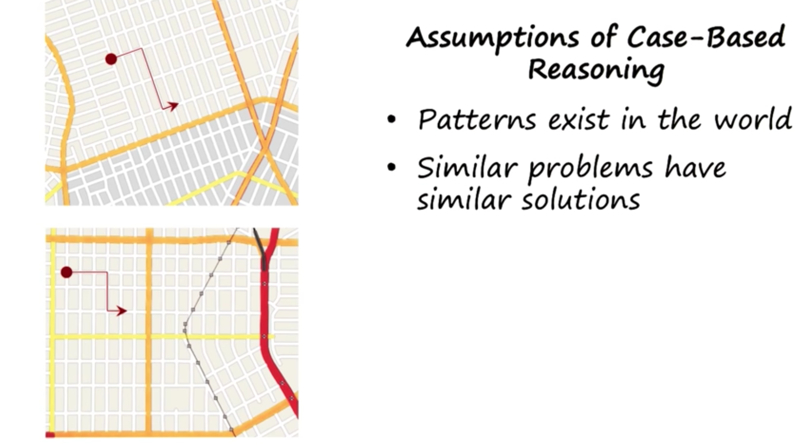
- the second assumption is not always valid (touch screen example and shoe lace example)
Case Adaptation
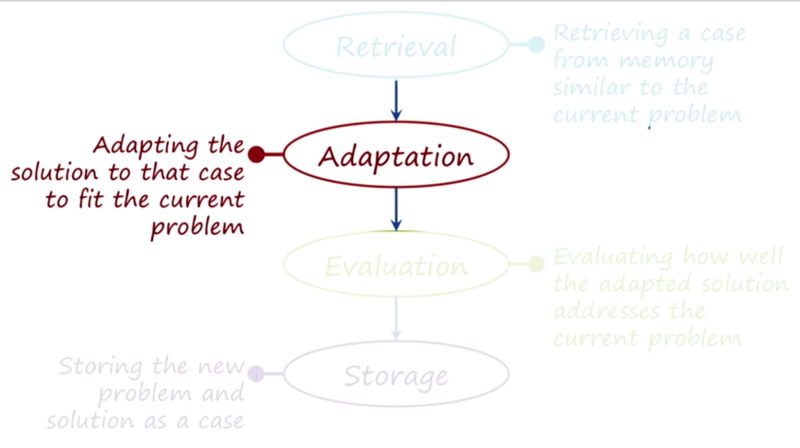
The adaption is usually very small tweak. e.g. cooking, programming. There are three ways to do case adaption
Case Adaptation by Model of the World
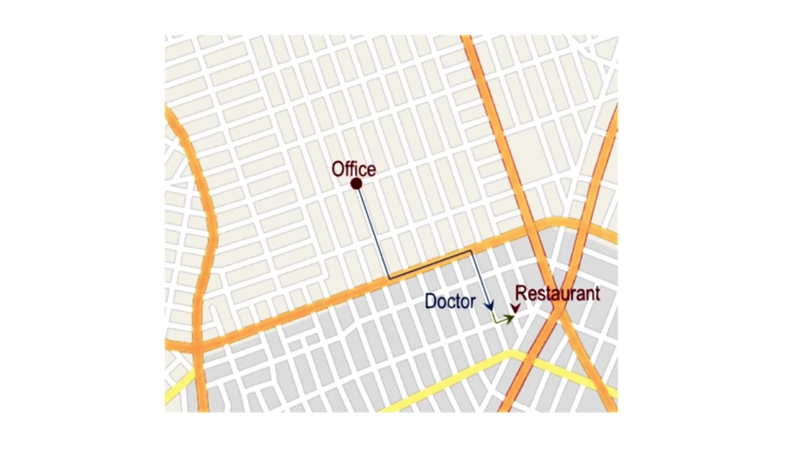
-
Examples: python API for programming.
-
use models to adapt, evaluate, and store cases.
Case Adaptation by Recursive
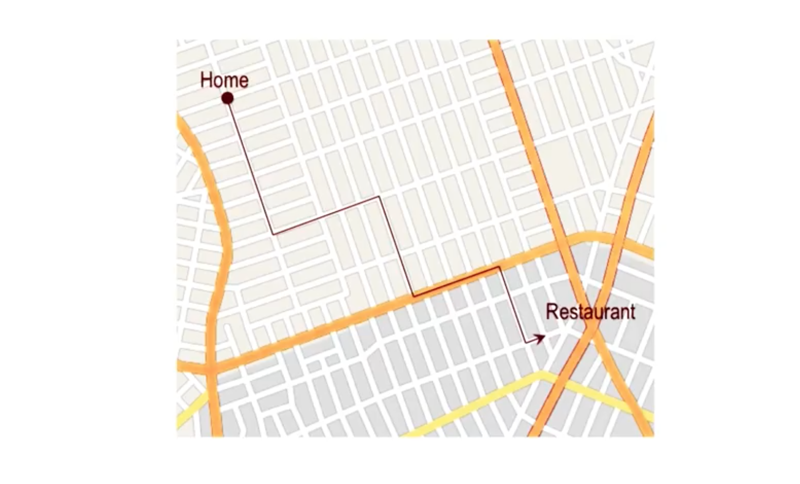
case was solved by dividing the problem into parts, and solve the sub-problems to get partial solution and then enter the unsolved part back the the agent to solve the rest of the question recursive.
- reading: Vattam, S. S., Helms, M. E., & Goel, A. K. (2008). Compound analogical design: interaction between problem decomposition and analogical transfer in biologically inspired design. In Design Computing and Cognition’08 (pp. 377-396). Springer Netherlands.
Case Adaptation by Rules
use heuristic rules to solve problems.
Case evaluation
evaluate the solutions from the program adaption
- Test the design with data
- evaluate the design by other designers, etc…
Case Storage
Case Storage by Index
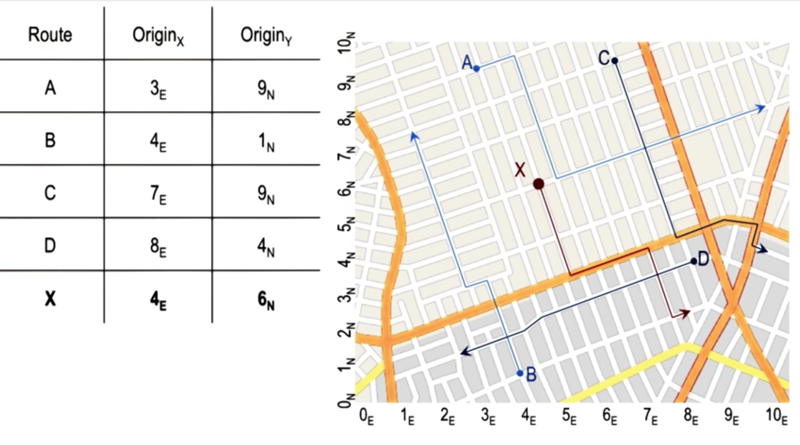
example
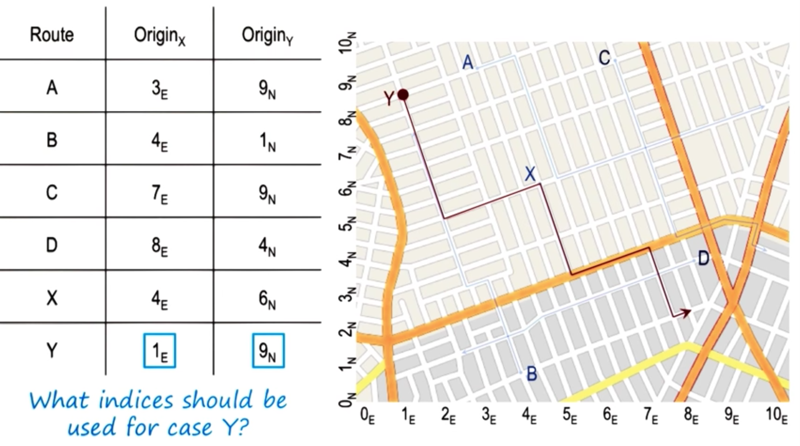
- When the dimension of the problem increase, the indexing method could become inefficient.
Case Storage by Discrimination
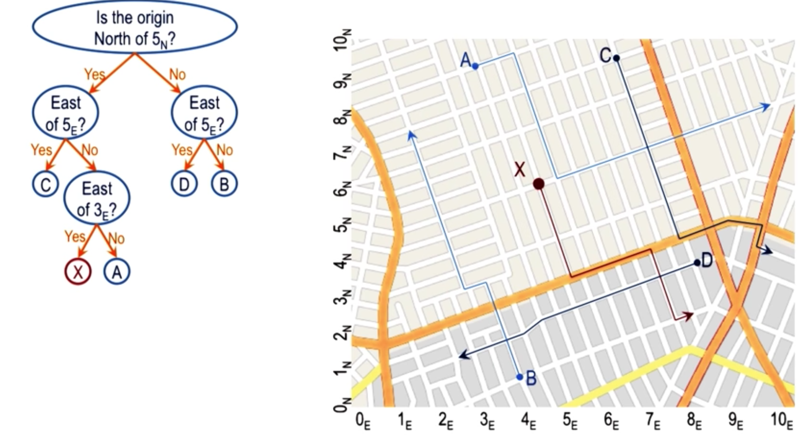
discriminate the cases by cutting points and build a tree from it.
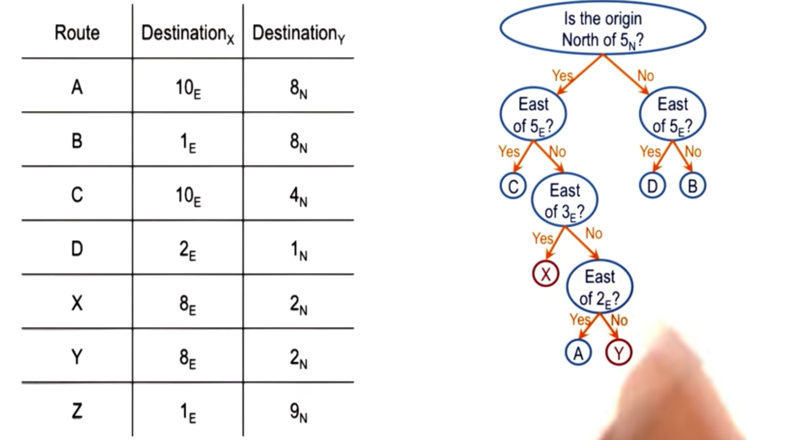
exercise
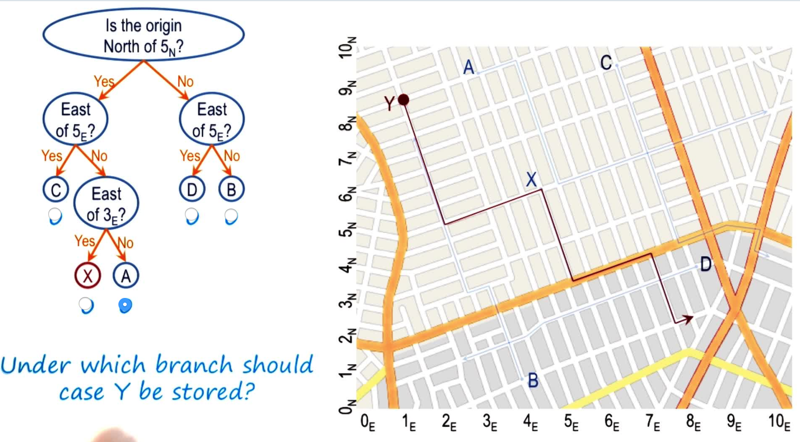
Where do Y belong to on the discrimination tree? By following the tree from the root, Y is with A. The the question becomes: how to discriminate Y from A.
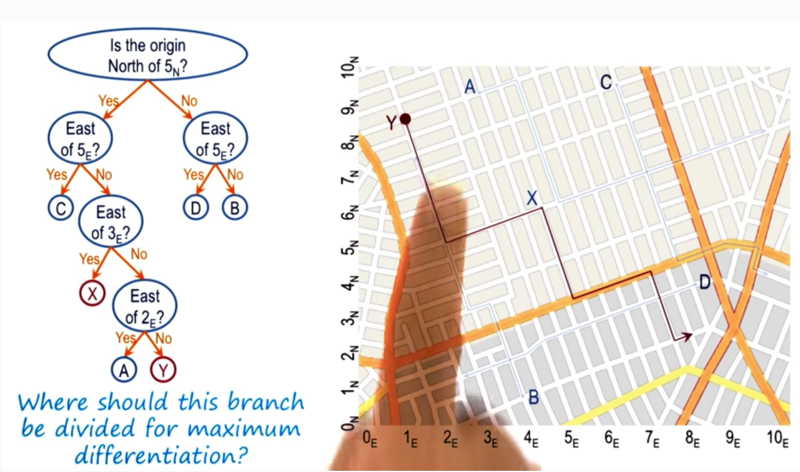
Case Retrieval Revisited
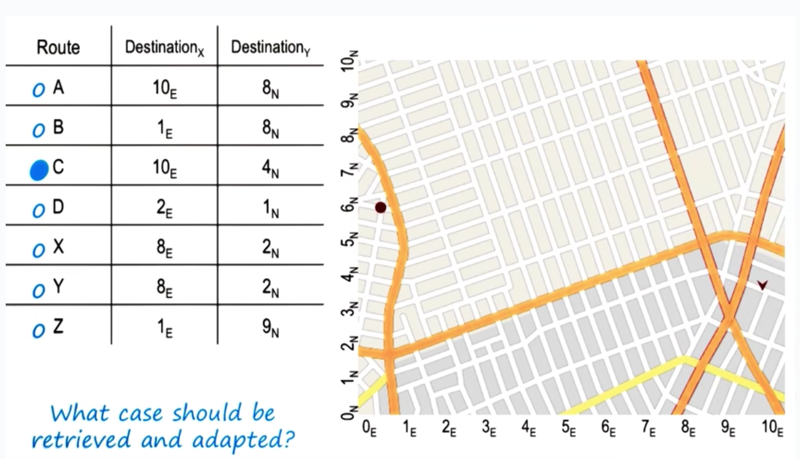
Advanced Case-Based Reasoning
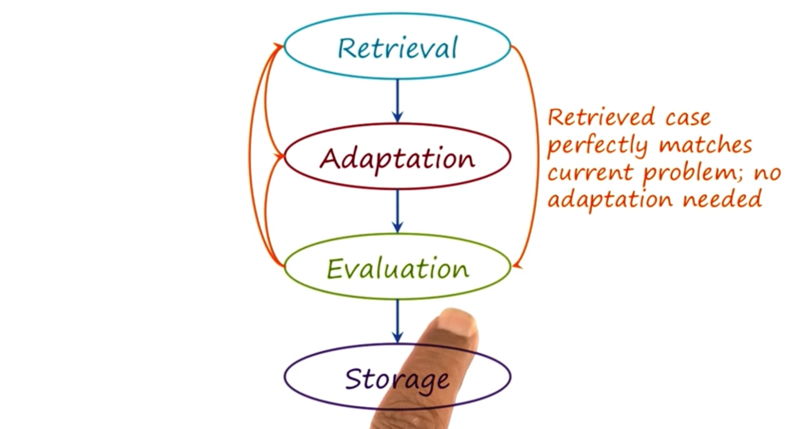
- if the evaluation result is bad: try redo adaption or retrieval again.
- storing failure cases might also useful to avoid failure ( learn the failure is learning). But storing failure must be very strategic.
Assignment

Wrap Up

The Cognitive Connection
Reasoning: tweak the solution and apply it Learning: evaluate the solution and store the ones that solve the new problem memory: memory enables the storage and retrieval of the cases.