- Lesson 4
- 02 - Lesson outline
- 03 - Relationship to Pandas
- 04 - Notes on Notation
- 5. Quiz: Replace a slice
- 06 - Creating NumPy arrays
- 07 - Arrays with initial values
- 08 - Specify the datatype
- 09 - Generating random numbers
- 10 - Array attributes
- 11 - Operations on ndarrays
- 12 - Quiz Locate maximum value
- 13 - Timing python operations
- 14 - How fast is NumPy
- 15 - Accessing array elements
- 16 - Modifying array elements
- 17 - Indexing an array with another array
Lesson 4
01 - What is NumPy

NumPy:
- is a Python library that acts as a wrapper around underlying C and Fortran code. Thus, very fast.
- focuses on matrices which are called in nd-arrays. It’s syntax is very similar to MATLAB,
02 - Lesson outline
If you’re familiar with NumPy (esp. the following operations), feel free to skim through this lesson.
- Create a NumPy array:
- from a pandas dataframe: pandas.DataFrame.values
- from a Python sequence: numpy.array
- with constant initial values: numpy.ones, numpy.zeros
- with random values: numpy.random
- Access array attributes: shape, ndim, size, dtype
- Compute statistics: sum, min, max, mean
- Carry out arithmetic operations: add, subtract, multiply, divide
- Measure execution time: time.time, profile
- Manipulate array elements: Using simple indices and slices, integer arrays, boolean arrays
03 - Relationship to Pandas
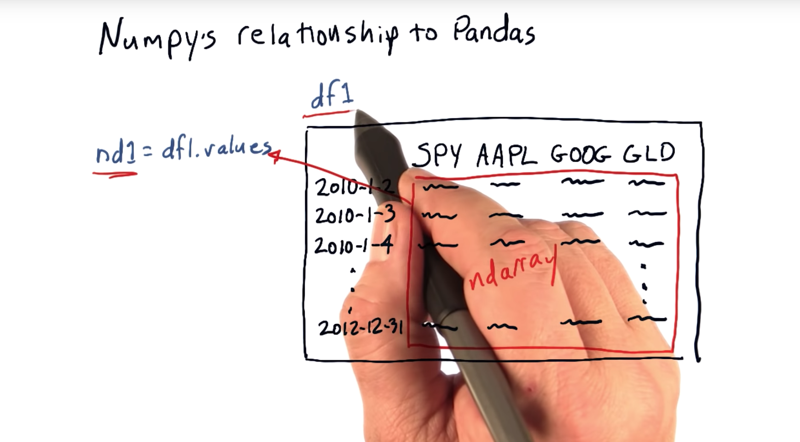
Pandas is a kind of wrapper for NumPy.
- Data frame is just a wrapper around this ndarray, access the columns with symbols and the rows by dates. And you CAN treat DF as an ndarray directly. *However, data frame allow us get many more routines.
04 - Notes on Notation
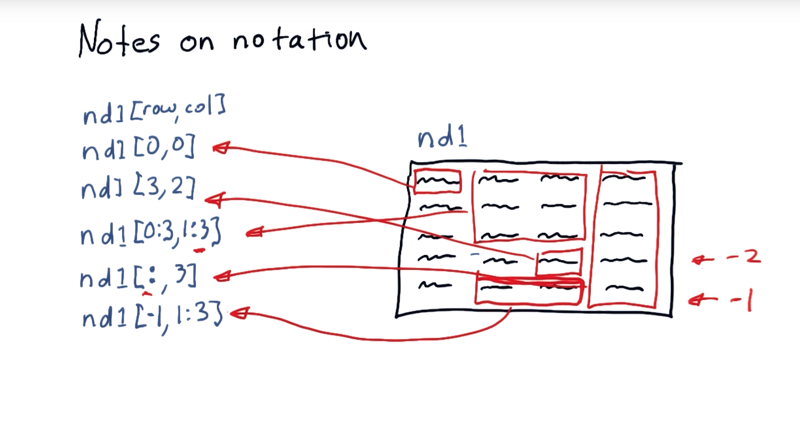
how to access cells within ndarray.
nd1(row,col)
- in NumPy, our columns and rows begin at 0. nd1[0,0] is the first item.
slicing: address sub portion of the nd array?
- Use the colon
:nd1[0:3,1:3]
[0:3,1:3] indicates starting at the zeroth row to just before the third and the first column to just before the third. The last value is one past the one that you actually want to include.
- use the colon by itself in the rows position to access all of the rows.
- Negative index: the last row = -1, the second to last row would be -2.
5. Quiz: Replace a slice
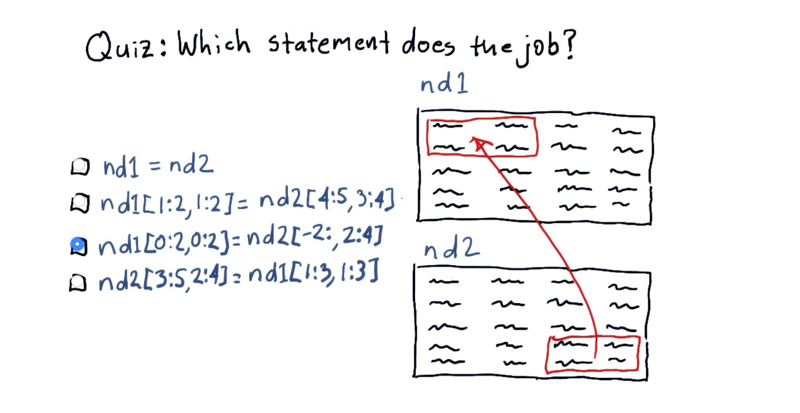 Suppose we have these two ND arrays, nd1 and nd2. And we want to replace some of the values in nd1, with these values from nd2.
Suppose we have these two ND arrays, nd1 and nd2. And we want to replace some of the values in nd1, with these values from nd2.
Which are correct?
06 - Creating NumPy arrays
- You can access the underlining NumPy array within a Pandas data frame using the values property.
Let’s create NumPy arrays from scratch.
one dimensional array from known values.

Use the array function to convert most array-like objects into an ndarray.
- The code above import the library numpy and rename it as np, then call a function np.array and pass a list which has value [2,3,4].
- np.array function can take as input a list, a template, or other sequences.
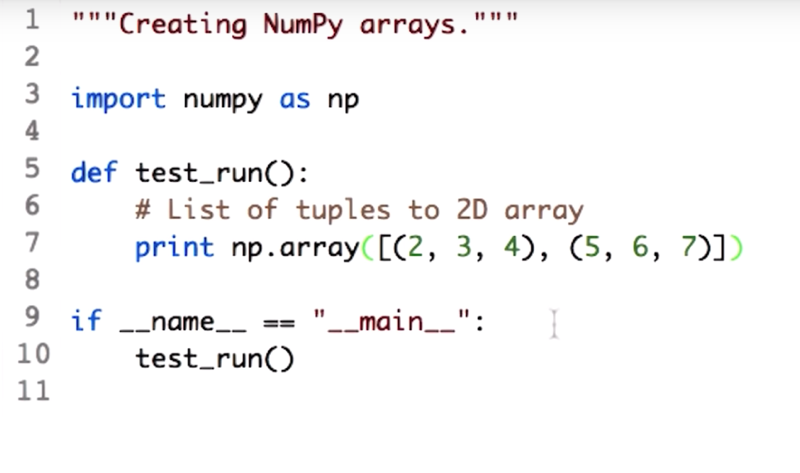
Now create a 2D array by passing in a sequence of sequences to the np.array function.
- the sequence of sequences are a list of lists or tuple of lists…
07 - Arrays with initial values

np.empty()function takes the shape of the array as input.- For the example above, we will create an empty array with five rows.
- Passing in a tuple with values 5 and 4 will create an empty array with five rows and four columns.
- just add another number to the sequence to create arrays of higher dimension.
- The empty array is not actually empty!!! the elements of the array read in whatever values were present in the corresponding memory location.
- And by default the elements are the floating points.

Next, we create an array full of ones.
using np.ones(), the above example creates an array of 5 rows and 4 columns with all the values equal to 1.
08 - Specify the datatype

What parameter do you need to add to this function to create an array of integers instead?
Documentation for the array.ones() function might be helpful.
Documentation: numpy.ones
NumPy User Guide: Data types
Documentation:
- numpy.empty
- numpy.ones
- numpy.zeros
- numpy.array
- numpy.ndarray (direct
ndarrayconstructor)
Answer: dtype is the parameter the values to be integers using NumPy data type np.int_.
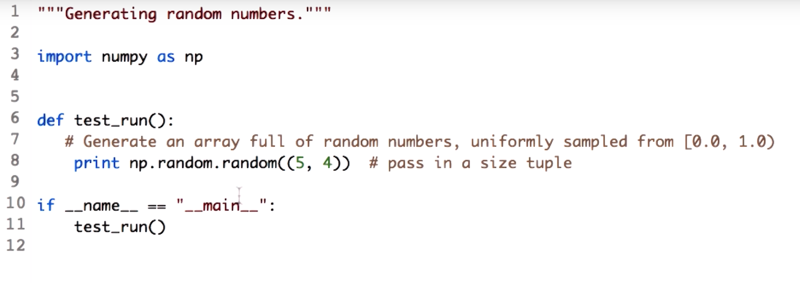
09 - Generating random numbers
Numpy functions to generate arrays filled with random values.
np.random.random(), np.random.rand(), np.random.normal(),
*the np.random.random() function generates uniformly sampled floating point values in [0.0, 1.0).
- Note: the array shape is a tupple, however, np.random.rand() accepts a sequence of numbers as arguments and straight of the tuple.
np.random.rand(5,4) is give the same results as np.random.random((5,4)). Numpy provides this to achieve compatibility with the Matlab syntax.
What if you wanted a sample from a different distribution?
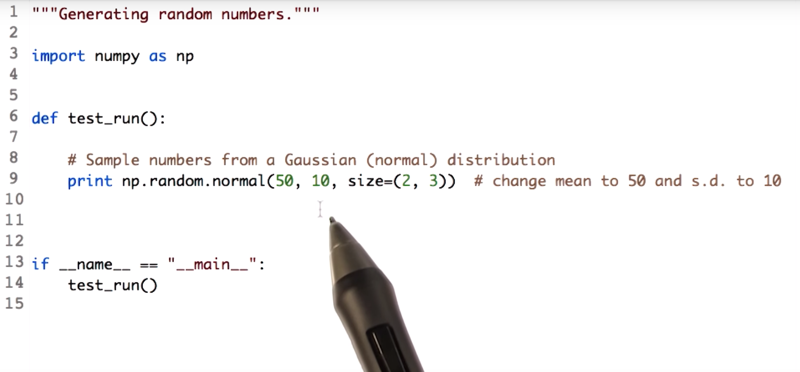
np.random.normal() function samples from normal distribution. the function also accepts mean and std of the distribution as input.
To generate integers, use the np.random.randint() function
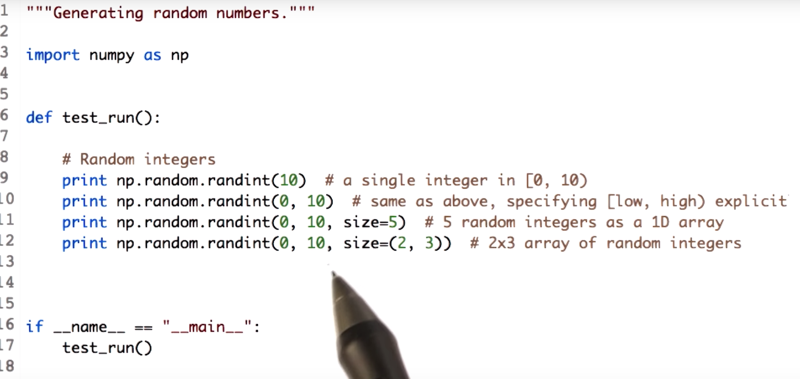
- Passing to values 0 and 10,
np.random.randint()WILL generate a single integer between the range 0 and 10. - Passing size= 5 to
np.random.randint()to generate 5 integers between 0 and 10. - passing a tuple value to the attribute size, which will create a 2d array with all the values between the range 0 and 10.
- Check out the random sampling routines on the numpy website for more distribution and usage radiations.
NumPy Reference: Random sampling
Sampling functions:
- numpy.random.random: Samples a Uniform distribution in [0.0, 1.0)
- numpy.random.rand: Like
random, but slightly different syntax- numpy.random.normal: Normal or Gaussian distribution
- numpy.random.randint: Integers from Uniform distribution
10 - Array attributes
Attributes like size and shape are very useful when you have to over array elements to perform some computation.
given ndarray a, ` a = np.random.random((5,4)):
a.shape will return the __shape__ of it as a tuple ( (5,4))
a.shape[0] will return number of rows (5)
a.shape[1] will return number of columns (4)
len(a.shape) and a.ndim will return the __dimension__ of the array, e.g. a has 2 dimensions
a.size returns the total number of elements in an array.
a.dtype` checks the data type of the values present in array A.
Attributes of numpy.ndarray:
- numpy.ndarray.shape: Dimensions (height, width, …)
- numpy.ndarray.ndim: No. of dimensions
= len(shape)- numpy.ndarray.size: Total number of elements
- numpy.ndarray.dtype: Datatype
Time: 00:02:33
11 - Operations on ndarrays
mathematical operations on np arrays
- Use
seedto generate random numbers
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(693)
a = np.random.randint(0,10, size = (5,4))
The output is an array with five rows, four columns, and all the values between the range 0 and 10. And since seed function is used, the random number generator with the constant, to get the same sequence of numbers every time.
- Summing
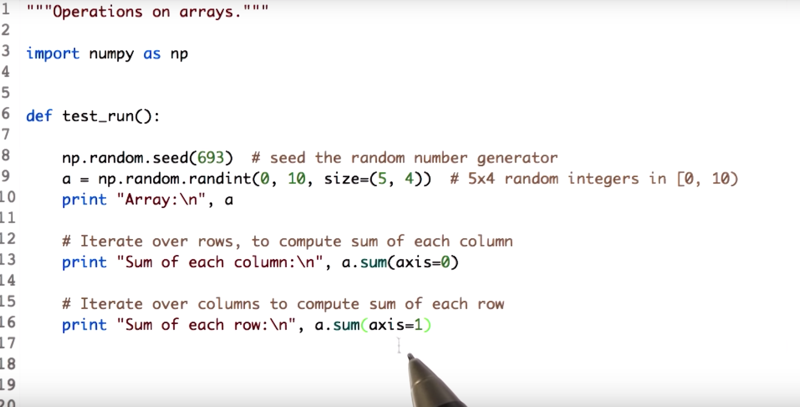
a.sum() sums all the elements in an array
a.sum(axis = 0) returns the sum of each columns.
a.sum(axis = 1) returns the sum of each rows.
- minimum, maximum, and mean of an array.
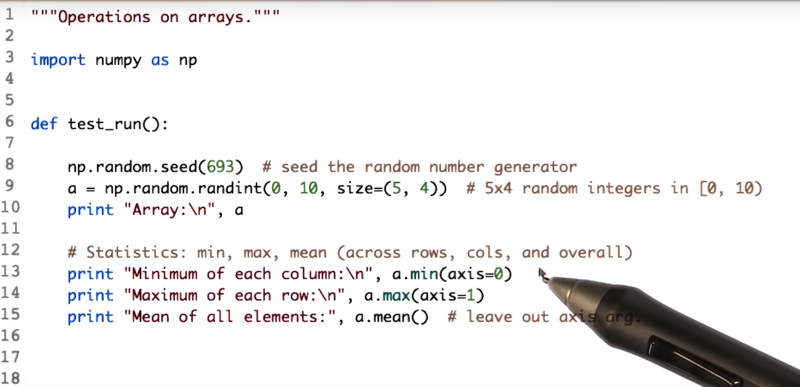
a.min(axis = 0) minimum of each column
a.max(axis = 1) the maximum of each row
a.mean() the mean of the entire array.
- More operations:
NumPy Reference: Mathematical functions
- numpy.sum: Sum of elements - along rows, columns or all
- numpy.min, numpy.max, numpy.mean: Simple statistics
Also: numpy.random.seed to (re)set the random number generator.
Time: 00:03:40
12 - Quiz Locate maximum value
- finding the position of some element in an array
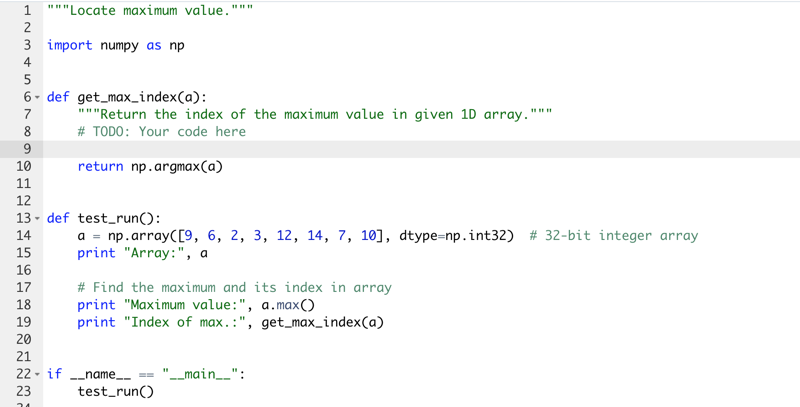
The answer could also be return a.argmax()
NumPy Reference: Sorting, searching, and counting
13 - Timing python operations
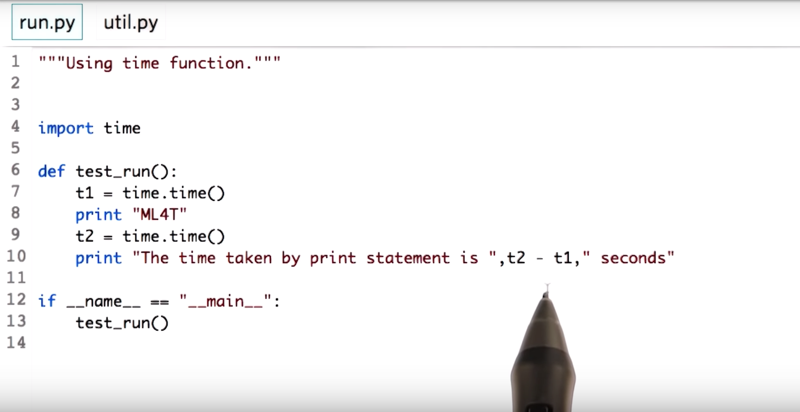
- how to time a particular operation.
the time library can help us know how fast our operation is.
capture the time snapshot before and after the operation is performed and subtract the two times.
Time: 00:00:56
Documentation:
- time.time: Time in seconds, as a floating-point number
14 - How fast is NumPy
This module demos how fast NumPy can perform certain operations. will skip this one. All you need to know is that NumPy is fast
Documentation:
- time.time: Current time in seconds (float value)
- timeit: Average execution time measurement
- profile: Code profiling
iPython “magics”:
15 - Accessing array elements
a[3,2]
a[0:2, 0:2]
a[:,0:3:2 n is to m is to t, will give you values in the range n before m, but in steps of size t, hence this statement will give you values of the column 0.Skip the values of the column one, and then give the values of the column 2.
NumPy Reference: Indexing
Note: Indexing starts at
0(zero).
Time: 00:02:29
16 - Modifying array elements
a[0, 0] = 1 This will give us access to the element at the position 0, 0 in the a and Using the assignment operator = to assign a value one to it.
a[0, :] = 2 can assign value of 2 to the entire row.
a[:, 3] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] can assign a list of values to a row or a column.
Time: 00:01:32
17 - Indexing an array with another array
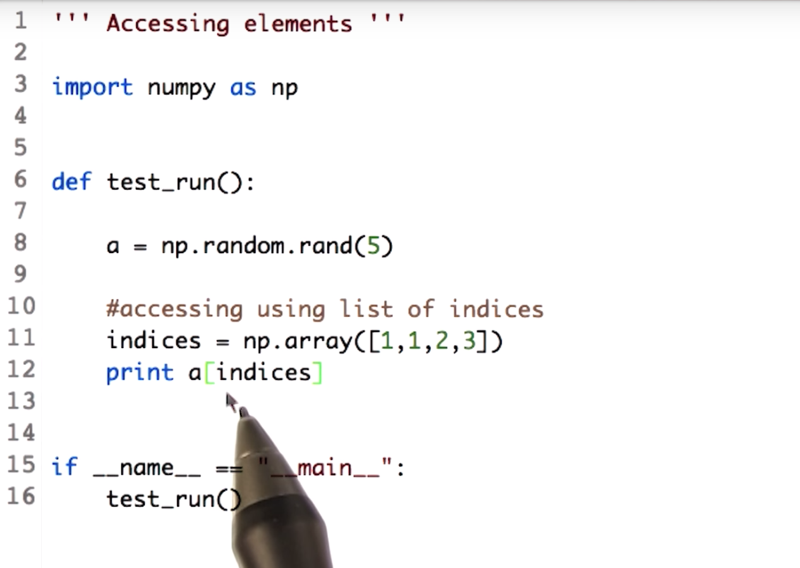
- NumPy array can be indexed with other arrays.
the length of the indices array and the returned array will be the same. Also it return value from array a at index 1,1,2,3.
NumPy Reference: Indexing
- Integer array indexing: Select array elements with another array
Time: 00:01:33
18 - Boolean or mask index arrays
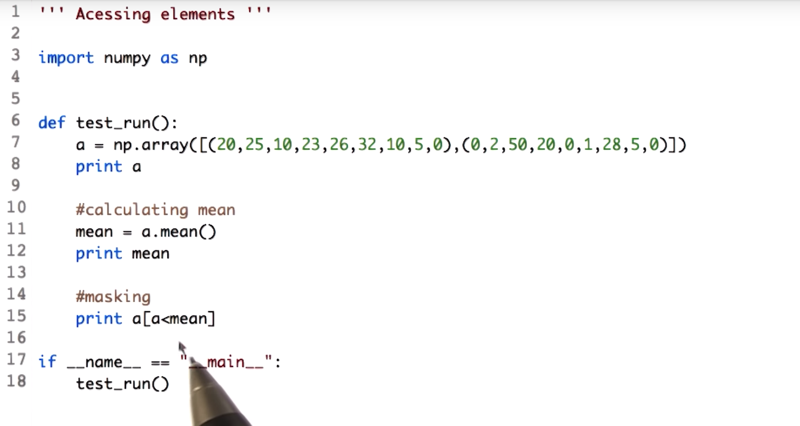
a[a < mean] for each value in array A, compare it with the mean, If it is less, we retain the value.
a[a < mean] = mean replace these values with the mean value.
NumPy Reference: Indexing
Time: 00:01:47
19 - Arithmetic operations
- Arithmetic operations on arrays are always applied element-wise.
2 * a it is element-wise multiplication.
a / 2.0 if the array and the divisor are integers, the output will also be integers. Using 2.0 instead of 2 as the divisor, we will get float values.

- important note: the shape of a and b should be similar before the operation a + b, else it will throw error.
a + b

a * b

a / b
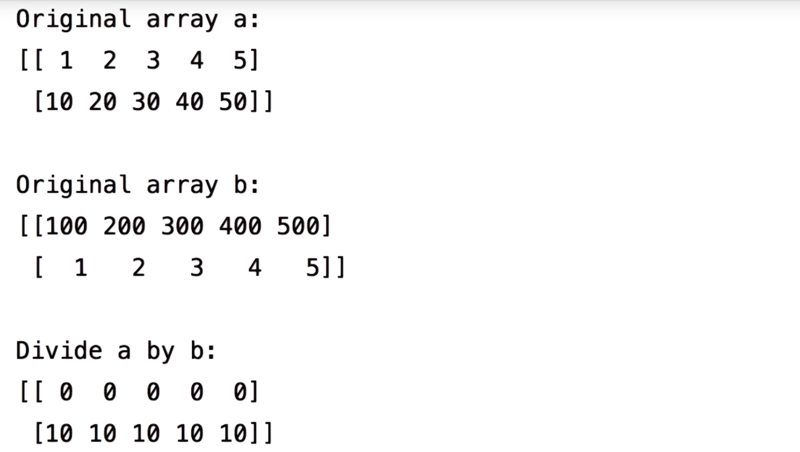
As seen before, since array a and b are integers, we get the final array in the form of integers as well. convert one of the arrays to float to get results as float .
20- Learning more NumPy
Resources from NumPy User Guide and Reference:
Time: 00:00:16
Total Time: 00:35:59
First Draft 2019-01-10